Jogging is one of the most popular and accessible forms of physical activity in the world. It can improve your health, fitness, mood, and overall well-being. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned runner, jogging can offer you many benefits and challenges. In this article, we will explore what jogging is, how to jog, some jogging tips, the benefits of jogging, how to prevent jogging injuries, and how jogging can help you lose weight.
What is Jogging?
Jogging is a form of running that is slower and less intense than sprinting or racing. Jogging is usually done at a pace of 6 to 9 km/h (3.7 to 5.6 mph), depending on your fitness level and goals. Jogging can be done on various terrains, such as roads, trails, tracks, or treadmills.
Jogging is different from walking in that both feet are off the ground at some point during each stride. Jogging is also different from running in that it involves less impact and stress on the joints and muscles. Jogging is considered a moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, which means it uses oxygen to produce energy and burns calories.
How to Jog
If you are new to jogging, you may wonder how to jog properly and safely. Here are some basic steps to follow:
- Warm up before you start jogging. You can do some dynamic stretches, such as leg swings, arm circles, or lunges, to loosen up your muscles and joints. You can also do some brisk walking for 5 to 10 minutes to gradually increase your heart rate and blood flow.
- Choose a comfortable pace that allows you to breathe easily and talk without gasping. You should be able to maintain this pace for at least 20 minutes without stopping. If you feel too tired or out of breath, slow down or take a break.
- Keep your posture upright and relaxed. Avoid hunching your shoulders, tensing your neck, or leaning forward or backward. Your head should be aligned with your spine, and your eyes should look ahead.
- Swing your arms naturally at your sides. Your elbows should be bent at about 90 degrees, and your hands should be relaxed. Avoid crossing your arms in front of your chest or clenching your fists.
- Land softly on the middle or front part of your foot, and roll through to your heel. Avoid landing on your heel or toe, as this can cause more impact and injury. Your feet should point straight ahead, not inward or outward.
- Push off with your toes and use your leg muscles to propel yourself forward. Avoid overstriding or bouncing too much, as this can waste energy and increase stress on your joints.
- Breathe deeply and rhythmically through your nose and mouth. Try to inhale for two or three steps and exhale for two or three steps. Avoid holding your breath or breathing too shallowly.
- Cool down after you finish jogging. You can do some gentle stretches, such as hamstring stretches, quadriceps stretches, or calf stretches, to relax your muscles and prevent stiffness. You can also do some slow walking for 5 to 10 minutes to lower your heart rate and blood pressure.

Jogging Tips
To make the most of your jogging experience, here are some jogging tips to keep in mind:
- Set realistic and specific goals for yourself. For example, you can aim to jog for a certain distance, time, frequency, or speed. You can also use a fitness app or a tracker to monitor your progress and achievements.
- Follow a jogging schedule that suits your level and lifestyle. You can start with jogging for 20 minutes three times a week, and gradually increase the duration, intensity, or frequency as you improve. You can also vary your jogging routes to avoid boredom and challenge yourself.
- Wear appropriate clothing and footwear for jogging. You should wear breathable, lightweight, and comfortable clothing that fits well and does not chafe or restrict your movement. You should also wear supportive and cushioned shoes that fit well and match your foot type and gait.
- Hydrate yourself before, during, and after jogging. You should drink water or sports drinks to replenish the fluids and electrolytes you lose through sweating. You should also avoid alcohol, caffeine, or sugary drinks that can dehydrate you or affect your performance.
- Eat a balanced diet that fuels your body for jogging. You should eat carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and fiber in moderate amounts and proportions. You should also avoid eating too much or too little before or after jogging.
- Listen to your body and adjust accordingly. You should pay attention to how you feel during and after jogging, and modify your pace, distance, frequency, or intensity if needed. You should also rest when you are tired, sick, injured, or sore.

Benefits of Jogging
Jogging can provide you with many physical, mental, and emotional benefits, such as:
- Improving your cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
- Strengthening your muscles, bones, joints, and ligaments and preventing or delaying the onset of osteoporosis, arthritis, and other degenerative diseases.
- Enhancing your respiratory system and increasing your lung capacity and oxygen uptake.
- Boosting your immune system and lowering the risk of infections, colds, flu, and allergies.
- Burning calories and fat and maintaining or losing weight.
- Regulating your blood sugar levels and preventing or managing diabetes.
- Improving your brain function and memory and preventing or delaying the onset of dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and other cognitive disorders.
- Elevating your mood and reducing stress, anxiety, depression, and anger.
- Increasing your energy and stamina and improving your sleep quality and quantity.
- Building your confidence and self-esteem and improving your body image and appearance.
- Having fun and enjoying nature, music, or socializing with other joggers.
Jogging for Weight Loss
Jogging can be an effective way to lose weight if you do it regularly and combine it with a healthy diet. Jogging can help you burn calories and fat while preserving your muscle mass. Jogging can also boost your metabolism and suppress your appetite.
To lose weight by jogging, you should follow these guidelines:
- Jog at least three times a week for at least 20 minutes each time. You can increase the duration, intensity, or frequency as you improve.
- Jog at a moderate pace that allows you to breathe comfortably but not easily. You should be able to talk but not sing while jogging. You can also try interval training, which involves alternating between fast and slow paces to burn more calories in less time.
- Eat a balanced diet that matches your energy needs and goals. You should eat enough carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and fiber to fuel your body and keep you satisfied. You should also avoid eating too much or too little, or skipping meals.
- Drink plenty of water before, during, and after jogging. You should drink at least 2 liters of water per day to stay hydrated and flush out toxins. You should also avoid drinking alcohol, caffeine, or sugary drinks that can dehydrate you or add extra calories.
- Track your progress and results. You can use a fitness app or a tracker to monitor your distance, time, speed, calories burned, and weight loss. You can also take measurements of your body parts, such as your waist, hips, thighs, and arms. You should also take photos of yourself before and after jogging to see the changes in your appearance.
- Reward yourself for your achievements. You can treat yourself to something you enjoy, such as a new outfit, a movie, a massage, or a vacation. You can also celebrate with your friends or family who support you and motivate you. You should also be proud of yourself for your efforts and hard work.
- Be consistent and patient. You should stick to your jogging routine and diet plan as much as possible. You should also avoid comparing yourself to others or expecting unrealistic results. You should remember that weight loss is a gradual and long-term process that requires dedication and perseverance.
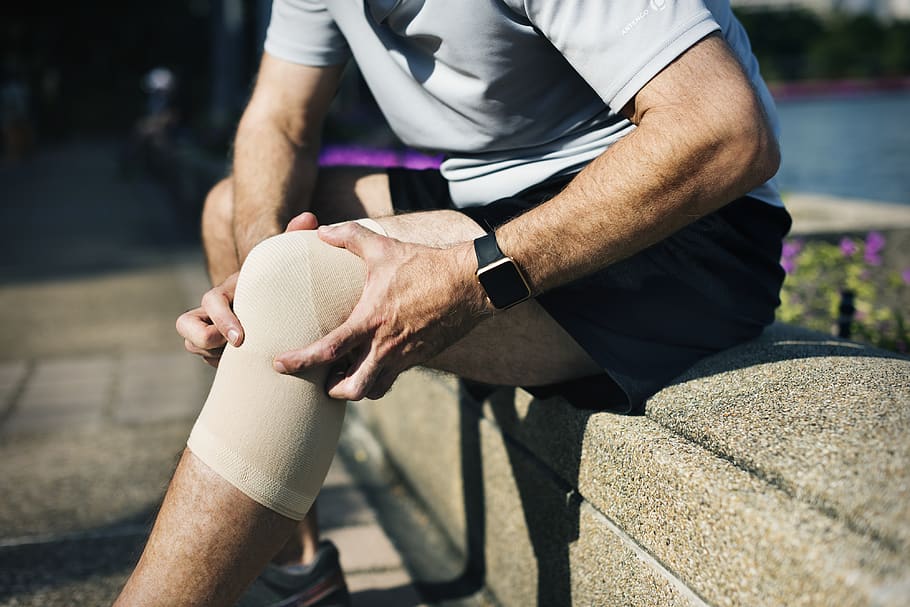

Jogging Injuries
Jogging is generally a safe and low-risk activity, but it can also cause some injuries if you are not careful or prepared. Some of the common jogging injuries include:
- Runner’s knee: This is a pain or inflammation in the front or side of the knee caused by overuse, misalignment, or weakness of the knee joint or surrounding muscles. It can be prevented by warming up properly, stretching regularly, strengthening the quadriceps and hamstrings, wearing supportive shoes, and avoiding downhill or uneven surfaces.
- Shin splints: This is a pain or tenderness along the inner or outer edge of the shinbone caused by overuse, stress fractures, flat feet, or tight calf muscles. It can be prevented by warming up properly, stretching regularly, strengthening the lower leg muscles, wearing supportive shoes, and avoiding hard or uneven surfaces.
- Achilles tendinitis: This is a pain or inflammation in the back of the heel or lower calf caused by overuse, tightness, or weakness of the Achilles tendon or calf muscles. It can be prevented by warming up properly, stretching regularly, strengthening the calf muscles, wearing supportive shoes, and avoiding uphill or uneven surfaces.
- Plantar fasciitis: This is a pain or inflammation in the bottom of the heel or arch of the foot caused by overuse, tightness, or weakness of the plantar fascia or foot muscles. It can be prevented by warming up properly, stretching regularly, strengthening the foot muscles, wearing supportive shoes, and avoiding barefoot or high-heeled shoes.
- Sprains and strains: These are injuries to the ligaments or muscles that support the joints caused by twisting, turning, or stretching too far. They can be prevented by warming up properly, stretching regularly, strengthening the muscles around the joints, wearing supportive shoes, and avoiding sudden or jerky movements.
How to Prevent Jogging Injuries
To prevent jogging injuries from happening or worsening, you should follow these tips:
- Warm up before you jog and cool down after you jog. This will prepare your body for jogging and prevent stiffness and soreness.
- Stretch before and after you jog. This will improve your flexibility and range of motion and prevent tightness and cramps.
- Follow a jogging schedule that matches your level and goals. This will help you progress gradually and safely and avoid overtraining or undertraining.
- Vary your jogging routine to avoid boredom and injury. You can change your pace, distance, frequency, intensity, terrain, or time of day to challenge yourself and have fun.
- Rest when you need to. You should take at least one day off per week from jogging to allow your body to recover and repair itself. You should also listen to your body and stop jogging if you feel pain, discomfort, or fatigue.
- Seek medical attention if you have a serious injury. You should consult a doctor if you have severe pain, swelling, bruising, bleeding, or infection in any part of your body. You should also follow their advice on how to treat and heal your injury.







